Lead & Your Health
Ok, lead was banned for good reason because lead is not required for any normal bodily function. It’s not in a multivitamin. Lead has a long history (dating back to Roman times) and has been used extensively by many industries. It is still used in some countries and in the United States has been found in household items including food.
The chart below shows how the United States was late to the game in banning lead as compared to other developed countries.

Unless you are taking chemistry you are not being bombarded with information regarding metals, good or bad, so what is lead? Lead is a naturally occurring heavy, in the color you will see bluish-grey that has a relatively low melting point (327°C). Roofs had lead solder during Ben Franklin’s time as the lead was commonly used in roof flashing. But we evolved and used lead in pipes for our drinking water and in paint in our homes to make the paint dry faster, and make the paint moisture resistant and long-lasting. Sure bridges, school buses, road paint, shot and ammunition, solder, fishing sinkers, ceramic glazes, dyes, and shielding to protect from radiation (x-rays, etc.) contained lead. Even with the push for EV’s the most widespread use of lead today is in vehicle batteries. So yes you have lead sitting in your garage or driveway.

So assuming you are not chewing on your car battery, how are you exposed to lead?
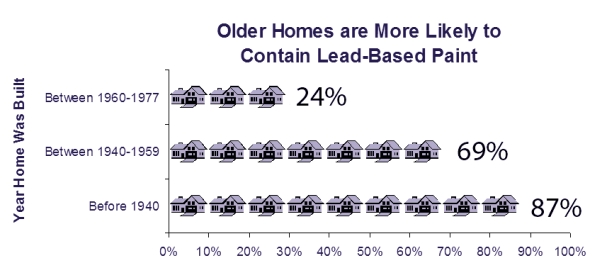
Since lead paint is estimated to be used in almost 90% of homes built before 1940, living in an older home likely exposes you to lead. Since lead was in paint you can encounter lead in paint chips or dust from friction surfaces where lead-painted windows and doors that rub liberate lead. That not counting the lead pipes in homes which were common well past 1940s.
In the outdoors or workplaces, you can encounter lead auto repair, metal recycling, lead-lighting, stained glass, firing and glazing pottery, soldering electronics, making fishing sinkers and renovating older homes, older furniture (sometimes called heirloom pieces), cars or boats coated with lead-based paint. Look you can go to a store and buy shiny glazed pottery made outside of the United States and it will have lead in it. Same thing with inexpensive imported jewelry.
Who is most at risk to lead?
To be fair and to explain this as simply as possible, an equal amount of lead will harm a child more than an adult simply based on the size of the human compared to the amount of lead exposure. If adults and children swallow the same amount of lead, about five times more is absorbed into the body by children.
Understand that kids are small and babies and small children can breathe and swallow lead while they play on the ground (lead is heavy and drops out of the air and stays on the floor). Lead has a sweet flavor and that only compounds children’s desire to ingest it.
How does lead enter and leave the body?
You can breathe lead when it is airborne, but you are most likely going to ingest lead by swallowing lead-bearing dust, soil, or paint chips. If lead is on your skin, only very small amounts of lead can pass into your bloodstream, but if it is not washed off, it can be accidentally swallowed. Most people have no concept of how many times their hands touch their mouth in a given day.
So once you consume a lead particle (let's agree lead exposure is normally a small gust particle) the amount of lead that actually gets into your blood depends on how old you are, when you last ate, and how well the lead particles dissolve in the stomach or lung.
So after lead is absorbed into your body it travels in your blood to soft tissues and organs, including liver, kidneys, brain, muscles, and heart. The lead can then be either stored or excreted into your urine and feces. The time it takes for most of the lead to be excreted depends on how long you have been exposed. If the lead is not excreted by the kidney or gut within a few weeks, the remaining lead moves to your bones and teeth.
Lead absorption depends really depends on a rather complex variety of factors, including the lead particulate size, the route of exposure, the health of the exposed individual, and the age of the individual.
-
Lead absorption is correlated to the route of exposure and the exposure particle size. For example, exposure to breathing in lead dust can result in higher absorption of lead than exposure to the equivalent amount of lead through ingestion. from chips (digestive route) of higher lead content paint.
-
Fact Adults typically absorb up to 20% of the ingested inorganic lead after a meal and up to 60-80% on an empty stomach.
-
Children absorb about 50% of the ingested lead after eating and can be as high as 100% on an empty stomach.
-
Most inhaled lead in the lower respiratory tract is absorbed.
-
Most of the lead that enters the body through ingestion is excreted in time through normal bodily bathroom functions.
Some lead can be stored for up to 30 years in bone. Lead in your bone can move back into the blood during pregnancy, breastfeeding, after breaking a bone, and due to osteoporosis. Lead absorbed by the mother can also pass through the placenta to the baby.
The rub with lead is if you do not know you are being exposed to lead, exposure will continue and an accumulation of lead will occur in the body, especially in bone.
Science focuses on the measurement of lead in your blood as the best gauge of lead exposure.
But lead is the equal metal, regardless of exposure pathway (breathing or swallowing) the effects of lead are the same. The central nervous system is the main target for lead toxicity in both adults and children. Long-term exposure in adults to low levels of lead have found to be associated with weakness in fingers, wrists, and ankles, headaches, fatigue, increases in blood pressure, anemia, and damaged nerve and renal function, it kind of sounds like just being an adult.
High levels of lead can damage the brain and kidney functions. If you have diabetes, you have a higher risk of adverse effects associated with the kidney.
Can lead affect the health of children?
100% of children are most at risk to lead. First, if the mother during pregnancy is exposed to lead, she will inadvertently feed the lead to the unborn child. Children are more susceptible to being exposed to lead. Once the child is born they grow at an accelerated pace, including their brains which lead can harm them by causing reduced growth, learning difficulties, behavioral problems, and reduced IQ in young children. Lead exposure can affect hearing and the nervous system.
What do I do if I think I have been exposed to lead?
Consult a doctor and have your blood checked for lead. If an elevated count is found, detective work occurs regarding where the lead exposure is originating from (could be several sources) and the remediation of those sources. Clearly, professional guidance is necessary.
Curren performs both Lead Risk Assessment as well as Lead Paint Inspections.
Call the Experts.
888-301-1050


