What are appropriate Due Diligence time frames?
One of the most common issues in buying and selling real estate is unrealistic due diligence time frames & settlement dates. Settlement dates that are set PRIOR to any due diligence being completed is the biggest failure. If you are involved in real estate and the due diligence finds an Area of Concern (AOC) or a Recognized Environmental Condition (REC) 80% of the time the settlement date needs to be pushed back.
Quick example, completed Phase I ESAs for a site in New Jersey and Pennsylvania, both found potential USTs. Both required a geophysical, at one of the sites the property owner of 29 years swore there were no tanks, but they had zero paperwork to support that statement. Fast forward three (3) tanks were found between the two sites. Now you have to get NJDEP & PADEP permits and register the regulated tanks, both sites took about 50 days to get government permits.
Understand that Due Diligence has Many Layers and steps.
Take for example a farm being purchased that required a Phase I ESA, the due diligence period was set for 30 days with settlement on the 31st day. The concern of the parties was whether the Phase I could be completed in 30 days, 90% of the time it can be, for the record most Phase I's can be completed in 2 weeks, sometimes 3 weeks. But the real issue is the parties left no time for a Phase II, if required, and most all farms would require some form of a Phase II and that's coming from 30 years of experience. Even if you tell people testing is likely going to be recommended, no one listens and no one extends the due diligence period, but everyone gets upset when they have to change the settlement date. Sure the seller could have done their own Phase I & II prior to selling the property and saved time and headache, unfortunately, few sellers are that forward thinking.
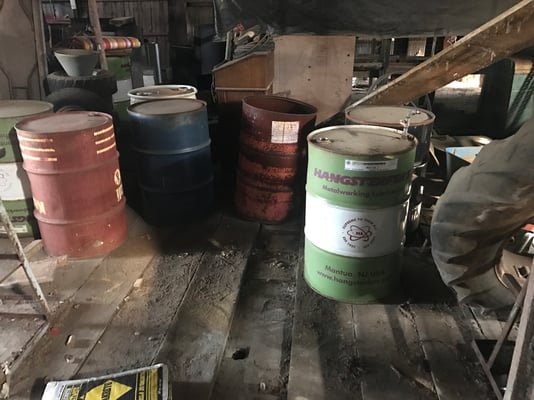

Let’s say, a property has had remediation completed, and multiple areas on a property were remediated. We just had a site that fits that bill. A Phase I is still completed to protect the buyer but the Phase I has to review state environmental reports that were submitted, which can take 4 weeks to get copies of reports. (Fact most owners have incomplete reports or cannot find the reports). Obtaining records from the government is not quick and yes a one (1) month wait is not uncommon. The 4-week due diligence period must be extended.
On the site we just dealt with, which was commercial, it was disclosed that multiple AOCs had been remediated and closed out with the state. But this site had other areas that were not remediated that warranted testing, multiple, like $42,000 worth of testing. Granted the property was 10.7 acres, listed for close to 3 million dollars, so it should not be surprising that AOCs existed on the property and were not evaluated by the seller, I mean few people who own real estate want to find a problem. The buyer still wanted to proceed with testing and purchase, and the seller did. Well, the seller ended the contract, they were concerned problems would be found they would have to address. Now, did the seller side warn them that this scenario was possible, hard to say but I would venture a guess the answer is no. Is the seller wise in thinking another buyer will come along to buy the property without testing? They can hope but are unlikely. The buyer was more than upset that a deal valued in the millions would be stopped in its tracks due to their desire to test and ensure they were not buying a contaminated property. The buyer also was willing to contribute to some amount of remediation.
But let’s say the deal kept moving forward and the seller gave another 30 days of due diligence. The testing could be completed in this 30-day window, but if remediation was warranted, 30 days is not enough. But the seller says we can price out cleanup and negotiate a price reduction within 30 days. Still an epic unrealistic situation as Phase II is just evaluating if contamination is present not the extent. Say three areas out of 14 need remediation (an unrealistic low number but just play it out). Your next step is to define the 4 areas which could take another 30 days maybe 90 depending on soil and groundwater. This situation actually played out on another site and the due diligence was 9 and 1/2 months.
Pro Tip
All you bankers, real estate professionals, sellers, buyers, and lawyers listen up. Ask your environmental professional what they would estimate for a reasonable due diligence, when a Phase I & II may be necessary. Before you ask do not give them your desired date of settlement, you will likely bias their answer. Although as environmental professionals we are not clairvoyant, we can assess sites from a desk, and utilize experience from other sites we have evaluated many times before to say you may want to budget 60 days or 90 days, if it's less, well then you can settle sooner. You should also consider if any cost sharing will occur with Phase II between buyer and seller and what the seller's pain point is on paying for remediation.
For example, the client had a retail strip of stores with historic groundwater contamination. The economical solution was to monitor the groundwater for 8 quarters to show a declining trend and permit the contamination in place. The 2-year budget was $86,000, which was also the amount the seller was willing to place in escrow after the sale for the buyer to use to pay for the work. But the $86,000 was a budget and could trend higher or lower. This confused the buyer as well as the fact that there would be costs after the site is signed off that the owner would be responsible for and this is assuming groundwater trends lower. Some sites do not and you need to perform remediation to push levels lower. This is another situation where all parties were not transparent regarding time frames and costs and what each party was willing to accept.
Last example and let me dumb this down for you.
A residence had a leaking tank, which was discovered during due diligence. The future cost of remediation was determined, what was not discussed was the time frame to remediate and when state would review and sign off (typically 2 weeks to 6 weeks to 2 months, depending on your state). Well at settlement these time frames were discussed and the buyer backed out at the settlement table. Now the blame on this one was the environmental company not timelining the remediation (parties not asking either). People went in with blinders on and the deal fell apart.
If your due diligence finds environmental concerns, know that environmental has no drive-through lane, no same-day delivery, heck not even a delivery date. Like medicine and law, it’s a practice, a somewhat inexact science, but data sets are out there if you are willing to listen. So rather than say due diligence is 30 days, ask what the consultant thinks is the reasonable time frame. Play out a couple of scenarios so all parties have an idea of what could happen, plan for the worst, and hope for the best.
Due Diligence Questions?
888-301-1050


 ental due diligence is critical for multi-tenant properties. A Phase I Environmental Site Assessment (ESA) is always the starting point, though the typical 2–3 week turnaround may be too fast for complex sites. In many cases, a Phase II ESA is also warranted, especially for older buildings or properties with tenants who may have generated hazardous waste.
ental due diligence is critical for multi-tenant properties. A Phase I Environmental Site Assessment (ESA) is always the starting point, though the typical 2–3 week turnaround may be too fast for complex sites. In many cases, a Phase II ESA is also warranted, especially for older buildings or properties with tenants who may have generated hazardous waste.



 The typical timeline for a Phase I ESA is two (2) to four (4) weeks. At Curren, we purchase historical records, which we usually receive within a week. When requesting public records (under the Open Public Records Act, or OPRA) from local towns or counties, we can expect a response within up to seven (7) business days. In New Jersey, for example, the law stipulates that a government agency must respond to an OPRA request no later than seven (7) business days after receiving it. Requests sent via email usually result in faster responses than those sent via mail. Day 1 of the response time starts the day after the custodian receives the request.
The typical timeline for a Phase I ESA is two (2) to four (4) weeks. At Curren, we purchase historical records, which we usually receive within a week. When requesting public records (under the Open Public Records Act, or OPRA) from local towns or counties, we can expect a response within up to seven (7) business days. In New Jersey, for example, the law stipulates that a government agency must respond to an OPRA request no later than seven (7) business days after receiving it. Requests sent via email usually result in faster responses than those sent via mail. Day 1 of the response time starts the day after the custodian receives the request.